
G: A list of supplementary groups which the user is also a member of. a: Add the user to the supplementary group(s). Now you need to add user to the sudo group using usermod command. bin/bash: Shell assigned to the User Step 4: Modify User Group cat /etc/passwd | grep -i test test:x:1000:1000:test,:/home/test:/bin/bash You can also verify other details as shown below.
Here you can grep test user from /etc/passwd file and check if the User is Created or not along with his home directory. You can verify user from /etc/passwd file.
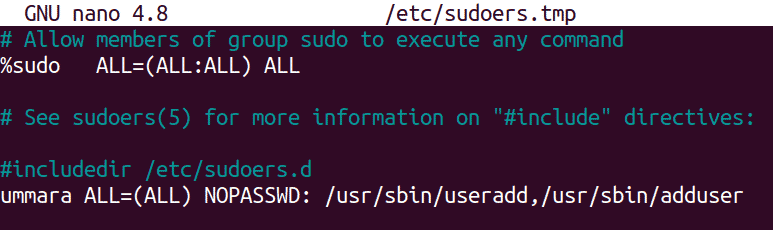
#Add user to sudoers password#
Passwd: password updated successfully Step 3: Verify User Retype the same password and press enter again. Provide a strong password when asked and press enter. You can set test user password using passwd command. More on useradd Man Page.īy default, if this option is not specified and CREATE_HOME is not enabled, no home directories are created. The files and directories contained in the skeleton directory (which can be defined with the -k option) will be copied to the home directory. m: Create the user's home directory if it does not exist. Here I am using root user to create test user. This needs to be done either through root user or any other user having sudo access. We will create a user test for our example.
#Add user to sudoers how to#
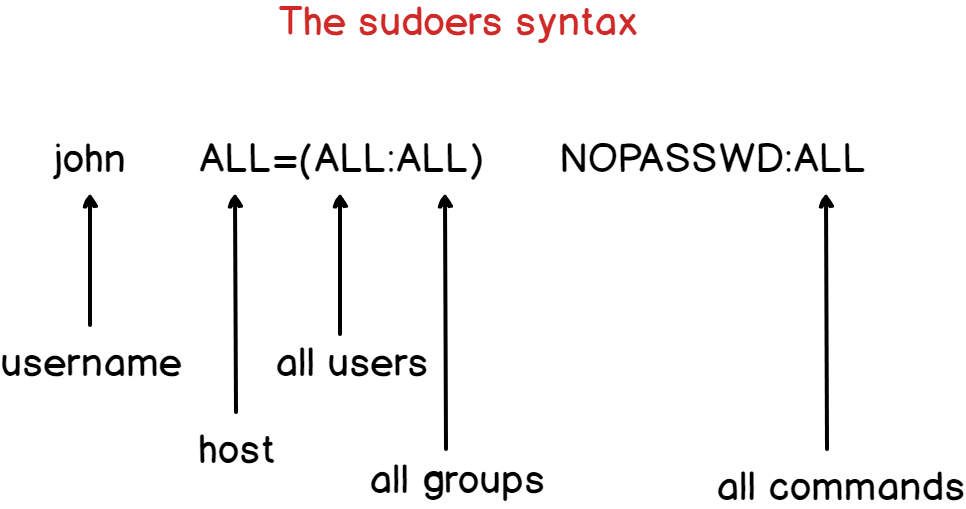
In those cases usually Linux Admin or System Admin provides sudo access to non privileged user to perform root operations as they cannot provide root user access.Īlso Read: How to Change Date/Time in RedHat/CentOS 7 Step 1: Create New Userįirst we need to create an user which can be given sudo access to perform administrative tasks. This is required in many Organization where some tasks cannot be performed without having root access. In many cases you might have seen that a non-privileged user has been given sudo access to perform root actions. In this tutorial, I will take you through Step by Step procedure to add user to sudoers on Ubuntu 18.04. Step 5: Add User to sudoers using visudo.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
